Expresando acuerdo
Con oraciones afirmativas - Affirmative (too/so)
- A: "I'm afraid of spiders." - Le tengo miedo a las arañas
B: "So am I." or "Me too." - Yo también - A: "I must hurry, it's late already" - Debo apurarme, ya es tarde
B: "Oh, Gosh! So must I." - Oh, ¡Dios mío! Yo también. - A: "You look good." - Te ves bien.
B: "So do you." or "You too." - Tú también. - A: "Mark lives in the suburbs." - Mark vive en los suburbios.
B: "So does Jane." - Jane también. - A: "We forgot to bring our umbrellas." - Olvidamos traer los paraguas.
B: "So did we." - Nosotros también. - A: "My child was sick yesterday." - Mi hijo estuvo enfermo ayer.
B: "So was mine." - El mío también.
Más ejemplos con oraciones afirmativas:
- I am hungry, and so are you. / you are too.
Tengo hambre y tú también. - My wife is a lawyer, and so am I. / I am too.
Mi esposa es abogada y yo también. - She was here yesterday, and so was he. / he was too.
Ella estuvo aquí ayer y él también. - I can swim, and so can my brother. / my brother can too.
Puedo nadar y mi hermano también. - I should study more, and so should you. / you should too.
Yo debería estudiar más y tú también. - They will go to the movies, and so will I. / I will too.
Ellos irán al cine y yo también. - Susan studies German, and so does Mary. / Mary does too.
Susan estudia alemán y Mary también. - John cleaned the house, and so did his wife. / his wife did too.
John limpió la casa y su esposa también. - They have gone out, and so has their son. / their son has too.
Ellos han salido y su hijo también.
Con oraciones negativas - Tampoco (either/neither)
- A: "I don't have any free time."
- No tengo tiempo libre.
B: "Neither do I." or "Nor do I." or "I don't either." or "Me neither."
- Yo tampoco. - A: "We don't smoke." - No fumamos.
B: "Neither does he." or "Nor does he." - Él tampoco. - A: "My husband wasn't very happy when I went shopping."
- Mi marido no estuvo muy contento cuando fui de compras.
B: "Neither was mine."
- El mío tampoco. - A: "They couldn't sleep last night." - No pudieron dormir anoche.
B: "Neither could I." - Yo tampoco. - A: "I can't speak French." - No hablo francés.
B: "Nor can we. Nosotros tampoco. - A: "David won't come to the party." - David no vendrá a la fiesta.
B: "Neither will John." - John tampoco.
Más ejemplos con oraciones negativas:
- I am not tired, and neither are my friends. / my friends are not either.
No estoy cansado y mis amigos tampoco. - I can't play chess, and neither can you. / you can't either.
No sé jugar al ajedrez y tú tampoco. - They won't attend the concert, and neither will I. / I won't either.
No irán al recital y yo tampoco. - I don't like novels, and neither does my girlfriend. / my girlfriend doesn't either.
No me gustan las novelas y a mi novia tampoco. - Jack didn't bring anything, and neither did his sister. / his sister didn't either.
Jack no trajo nada y su hermana tampoco. - She has not seen that film yet, and neither has her boyfriend. / her boyfriend hasn't either.
Ella no ha visto la película aún y su novio tampoco. - They don't have money, and neither do we. / we don't either.
No tienen dinero y nosotros tampoco. - Bill hadn't been there, and neither had his family. / his family hadn't either.
Bill no había estado allí y su familia tampoco.
a) Jim goes to school everyday. Mary. Mary .
b) Carol studied Biology. Paul. Paul .
c) Kaique is a very good student. Tati. Tati .
d) Vinicius can´t play the guitar. Antonio. Antonio .
e) Mariana bakes delicious cakes Tamires. Tamires .
f) Adriano will sing tomorrow Roger. Roger .
h) Jonathan did the homework Solemar. Solemar .
i) Erick has told a funny joke Sarah. Sarah .
j) They didn´t eat the salad I. I .
k) My mother hasn´t finished the juice my sister. My sister .
l) Lisa and Ann don´t go to the party they. They .
m) I would travel to Bali we. We .
n) We will have lunch together she. She .
2) Agree with the statements.
a) I worked hard last week..
b) My sister has got a new job .
c) My friends haven´t gotten married yet .
d) Kim is going to have a baby .
e) They love studying English.
f) They didn´t go to the mall last holiday. .
g) My parents will travel on Christmas .
h) They aren´t going to the concert
i) Rick speaks Spanish .
j) Nick is a good singer .
- MÁS EJERCICIOS too-either
- Y MÁS so-too-neither-either

Either and neither are singular concepts. They can be thought of as the opposite of the word both.
The word either can be an adjective or a pronoun. It meansone or the other of two people or things. Either is singular.
The word neither can also be an adjective or a pronoun. It means not the one nor the other of two people or things; i.e., not either. Neither is also singular.
Examples:
Examples:
Either crumpets or cake is sufficient.
(  under standard convention; should be are sufficient)
under standard convention; should be are sufficient)
( under the proximity rule – cake governs is because it is the nearest element.)
under the proximity rule – cake governs is because it is the nearest element.)
There was neither ice-cream nor chocolates at the party.
(  under standard convention; should be were because ofchocolates is a plural word.)
under standard convention; should be were because ofchocolates is a plural word.)
( under the proximity rule – ice-cream governs wasbecause it is the nearest element.)
under the proximity rule – ice-cream governs wasbecause it is the nearest element.)
The word either can be an adjective or a pronoun. It meansone or the other of two people or things. Either is singular.
The word neither can also be an adjective or a pronoun. It means not the one nor the other of two people or things; i.e., not either. Neither is also singular.
Examples:
- Either car is available.
 (This is either as an adjective.)
(This is either as an adjective.)
- Either of the cars is available.
 (This is either as a pronoun.)
(This is either as a pronoun.) - Neither man is suitable.
 (This is neither as an adjective.)
(This is neither as an adjective.)
- Neither of the men is suitable.
 (This is neither as a pronoun.)
(This is neither as a pronoun.)
Singular Verb with Singular Elements
If the pairings either/or (often the either is omitted) orneither/nor form part of the subject of a verb and both elements are singular, then the verb must be singular too. For example:- Neither Mark nor Dawn is at the function.
 (As Mark is singular (i.e., one person) and Dawn is singular, then is is correct. (The plural version are would be wrong.)
(As Mark is singular (i.e., one person) and Dawn is singular, then is is correct. (The plural version are would be wrong.) - Neither Dickens nor Thackeray was a panderer to the public taste.
 (As Dickens is singular and Thackeray is singular, was is correct; i.e., were panderers would be wrong.)
(As Dickens is singular and Thackeray is singular, was is correct; i.e., were panderers would be wrong.) - Either the clerk or the secretary has the keys to the Rover.
 (As clerk is singular and secretary is singular, has is correct; i.e., have would be wrong.)
(As clerk is singular and secretary is singular, has is correct; i.e., have would be wrong.) - Either a mouse or a rat eats the cable at night.

- Neither Simon nor Gary do as they are told.
 (As Simon is singular and Gary is singular, do is wrong. It should be does. Be mindful that you sometimes have to look further down the sentence too. This should be does as he is told.
(As Simon is singular and Gary is singular, do is wrong. It should be does. Be mindful that you sometimes have to look further down the sentence too. This should be does as he is told.
Plural Verb with a Plural Element
If the pairings either/or (often the either is omitted) orneither/nor form part of the subject of a verb and at least one of the elements is plural, then the verb must be plural too. For example:- Neither the lawyer nor the detectives are able to follow the sequence of events.
 lawyer (singular – i.e., one person), detectives (plural - i.e., more than one person), are (plural - i.e., not is)
lawyer (singular – i.e., one person), detectives (plural - i.e., more than one person), are (plural - i.e., not is) - There were neither cakes nor ice-cream at the party.

- Neither the firemen nor the policemen know him.
 (i.e., not knows)
(i.e., not knows) - Either the budgies or the cat has to go.

Proximity Rule
Not all grammar conventions agree with the ruling above. In fact, there is notable leniency on whether to use a plural or singular verb when one of the elements is plural. Under the proximity rule, the verb is governed by the element nearest to it.Examples:
 under standard convention; should be are sufficient)
under standard convention; should be are sufficient)(
 under the proximity rule – cake governs is because it is the nearest element.)
under the proximity rule – cake governs is because it is the nearest element.) under standard convention; should be were because ofchocolates is a plural word.)
under standard convention; should be were because ofchocolates is a plural word.)(
 under the proximity rule – ice-cream governs wasbecause it is the nearest element.)
under the proximity rule – ice-cream governs wasbecause it is the nearest element.)
ELEMENTS?
The elements are the words which follow either, or, neither or nor. (The elements are in bold in the first example below:
The elements are the words which follow either, or, neither or nor. (The elements are in bold in the first example below:
- Neither Mark nor Dawn is at the function. (elements in bold)
- Either tea and crumpets or cakeare sufficient. (elements in bold)
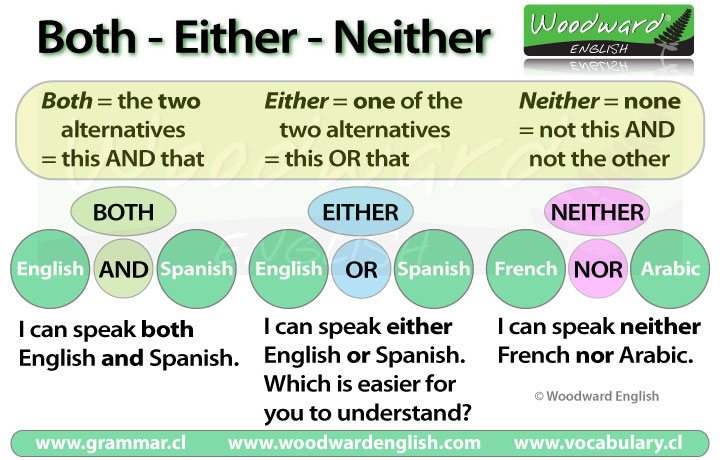
EXPLANATION
Too/either and so/neither are used to express our agreement to what another person has said.
Too is used when the verb is in the affirmative form. For example:
A: I have a red Ferrari
B: I have one, too
Either is used when the verb is in the negative form. For example:
A: I don't have a Ferrari
B: I don't have one either
But in English, we don't need to use long replies to express our agreement. This is not necessary because our agreement is with the entire sentence, so we use an auxiliary:
do/does when the verb is in the simple present
are/is when the original verb is in the present continuous
will when the original verb is in the future
have/has when the original verb is in a perfective tense
a modal when the original verb uses a modal, etc.
Too/so are used when we agree in the affirmative. For example:
A: I have an SUV (sport utility vehicle, a family car)
B: I have one too OR So do I
Either/neither are used when we agree in the negative. For example:
A: I don't have a bike
B: I don't have one either OR Neither do I
When we use so/neither, the verb must go in the affirmativeform and the order of the sentence takes the form of a question. More examples:
So must I
Neither will they
So should I
Neither are we
So is she
Neither are Peter and Susan
So do I
Neither will he
So can we
Neither could they
Can you find the first part of the aforementioned phrases with so and neither?
IMPORTANT!!!
So, too, either and neither have other functions in English. We will study them in the following sessions.
PRACTICE
- http://www.eslbee.com/cobaq/quizzes/13_so_too_neither.htm
- http://www.eflnet.com/grammar/soneithertut.php
- http://www.eflnet.com/grammar/soneither1.php
- http://www.learn-english-today.com/lessons/lesson_contents/so_neither-ex.htm
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-49198.php
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-68857.php
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-57421.php
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-69398.php
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-67793.php
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-58137.php
- http://www.proprofs.com/quiz-school/quizshow.php?title=lesson-76-too-so-either-neither&quesnum=1
GO FOR IT
Sometimes, it may sound wrong to use the singular form of the verb. Be confident and, if both elements are singular, use the singular form.
- Neither Jeremy nor Sarah was in the shop at the time of the theft.
 (i.e., not were in the shop)
(i.e., not were in the shop)
- CLICK TO OPEN AND STUDY
- Either/or and neither/nor (beware the double negative)
- List of easily confused words



No hay comentarios:
Publicar un comentario