Formación del "present continuous":
se construye con el presente del indicativo del verbo "to be", en su función de verbo auxiliar, y el "present participle" ( = gerundio) del verbo principal.
Examples:
- You are watching TV.
- Are you watching TV?
- You are not watching TV.
USE 1 Now

Se utiliza para describir acciones que se están desarrollando en este mismo momento:
I am reading a book. = Yo estoy leyendo un libro (en este preciso instante)
You are playing football. = Tú estás jugando al futbol
I am reading a book. = Yo estoy leyendo un libro (en este preciso instante)
You are playing football. = Tú estás jugando al futbol
USE 2 Longer Actions in Progress Now

También se utiliza para describir acciones que se están desarrollando alrededor del momento en el que se habla, se mira,aunque no necesariamente en ese preciso instante:
I am studying French. = Yo estoy estudiando francés (me he matriculado en una academia, pero no necesariamente en este preciso momento estoy con los libros de francés)
I am looking my favorite tv show = Estoy viendo my show favorito de television.
USE 3 Near Future

Asimismo, se utiliza para describir una acción que va a tener lugar en el futuro próximo y sobre la que se ha tomado una resolución firme. En este caso, siempre se tiene que mencionar el tiempo en el que se va a desarrollar la acción:
I am going to London next week. = Yo voy a Londres la próxima semana (la acción se va a desarrollar en el futuro próximo y existe una decisión firme por mi parte de llevarla a cabo)
USE 4 Repetition and Irritation with "Always"

Otro uso del presente continuo es para describir acciones que se vienen repitiendo con frecuencia; en este caso, la oración viene acompañada del adverbio "always" (siempre):
He is always working. El está siempre trabajando (con el significado de que trabaja frecuentemente, quizás, incluso, excesivamente)
Para ver mas sobre los usos de este tiempo verbal -Present Continuous- ve a esta página que tambien incluye ejercicios on line:
http://www.englishtenseswithcartoons.com/tenses/present_continuous
Comparemos con los usos del otro modo del tiempo presente, el Simple Present:Ambos verbos se utilizan para describir acciones presentes, si bien con diferentes matices.
a) Present continuous
a.1) Describe acciones que están ocurriendo en ese preciso momento.
I am reading the newspaper (lo estoy leyendo ahora)
a.2) También puede describir acciones que ocurren alrededor del momento actual, aunque no precisamente ahora.
I am planning a trip to Egypt for this summer (por ejemplo, le estoy contando a un amigo que estoy planeando un viaje; no es que lo esté planeando en ese preciso momento)
b) Present simple
b.1) Describe acciones habituales, actuales, generales, que no tienen porqué estar ocurriendo en ese preciso momento.
I work in a bank
I speak English very fluently
In Madrid people drive very fast
b.2) Describe también acciones que se repiten periódicamente, acciones rutinarias.
Every morning I have a meeting with my boss at 8 o'clock
I play tennis every Sunday
Algunos verbos no se suelen utilizar en tiempo continuo, por lo que en estos casos hay que emplear el "present simple":
Verbos que describen acciones de los sentidos: feel, hear, see, smell...
Verbos de sentimiento / emoción: like, love, hate, want, wish, fear, desire, detest, dislike...
Verbos de acciones mentales: agree, believe, forget, know, remember, think (=tener una opinion), understand, realize...
Verbos de posesión: belong, own, posess...
Por último, decir que estas dos formas verbales se emplean a veces para describir acciones futuras.
Ahora, para repasar y aplicar, ve a esta página a hacer un ejercicio:
We are studying the present continuous of the English verbs. (Estamos estudiando el presente continuo de los verbos ingleses)
Some verbs have certain spelling changes when adding "-ing": If the verb ends in "-e", we will drop the "e" and then we will add "-ing".
Example
I dance in the disco. (Bailo en la discoteca)
I am dancing in the disco. (Estoy bailando en la discoteca)
If the verb consists of only one syllable and the last three letters are: consonant plus vowel plus consonant, we will double the last consonant of the verb then add "-ing".
Example
I plan my weekend ahead. (Planeo el fin de semana que viene)
I am planning my weekend ahead. (Estoy planeando el fin de semana que viene)
PRACTICA CON ESTOS ENLACES EL PRESENTE SIMPLE Y EL CONTINUO.
RECUERDA QUE LAS 'TIME EXPRESSIONS' Y LOS ADVERBIOS DE FRECUENCIAS TE DAN PISTAS!!!
- http://www.inglesmundial.com/B9/grammar.htm
- http://ww2.college-em.qc.ca/prof/epritchard/pcvspsqk.htm
- http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/simcon1.htm
- http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/simcon2.htm
- http://www.englishpage.com/verbpage/verbs1.htm
- http://a4esl.org/q/h/vm/sp_or_pc.html
- http://www.isabelperez.com/happy/tenses/exercises/present_5.htm
- http://www.isabelperez.com/happy/tenses/exercises/present_6.htm
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-13689.php
- http://www.tolearnenglish.com/exercises/exercise-english-2/exercise-english-13846.php
- http://perso.wanadoo.es/autoenglish/gr.prescon.i.htm
- http://www.englishclub.com/grammar/verb-tenses_present-continuous_quiz.htm
- http://nea.educastur.princast.es/repositorio/RECURSO_ZIP/1_jantoniozu_Clothes/Tema_9_1%BAESO/Quiz/activ_5/quiz3/quiz%203.htm
- http://school.discoveryeducation.com/quizzes17/jaeckerly/prescont.html
- http://www.learn-english-online.org/Lesson7/TestIt/PresCont1.htmhttp://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/simcon1.htm
- http://esl.about.com/library/beginner/bl_bgprescont.htm
- http://web2.uvcs.uvic.ca/elc/studyzone/330/grammar/simcon1.htm
- http://cadnina.glogster.com/glog-4801/
PRESENTE ENFÁTICO
Esta forma se usa cuando se quiere enfatizar o recalcar a una afirmación. La forma enfática se obtiene mediante el auxiliar 'do'. Su construcción es:
sujeto + auxiliar + forma básica
I do study / ¡Yo estudio! (realmente estudio, de verdad que estudio)| Escríbe el tiempo verbal correcto en las siguientes frases: | ||
| 1. John to Mary now (talk) 2. I television every night. (watch) 3. The children usually to bed at nine o'clock. (go) 4. a book at the moment?. (Richard read) 5. They to the theatre very often. (not go) 6. I at the moment. (not study) 7. I English, although I at the moment. (not speak) / (study) 8. I in Valencia, though I in Madrid at the moment. (live) / (stay) 9. I in a hotel at the moment, although I my own apartment. (stay) / (have) 10. She from Chile, though she in New York just now. (come) / (live) |
Present Continuous Forms
| Positive | Negative | Question |
|
|
|
¿Todos los verbos pueden conjugarse en este tiempo? Algunos verbos no se prestan a esta conjugacion. Veamos que hay diferentes tipos de verbos, en esta página: http://www.englishpage.com/verbpage/types.html
EXERCISES Si comete errores, se recomienda repasar los temas y volver a realizar los ejercicios.

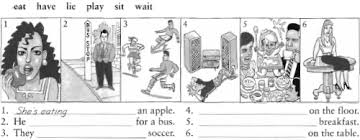
What is she doing?
She (read) a book.

What is she doing?
She (have) a drink.

What are they doing?
They (dance)

What is he doing?
He (write) a letter.
What is he doing?
He (work)

What are they doing?
They (watch) the eclipse.
Elija la opción más adecuada para responder a las siguientes preguntas.
Is Brian reading a book?
Yes, he does.
Yes, he is.
What is Brian reading?
He's reading a magazine.
Yes, he does.
Is Susan writing a poem?
No, she is not.
Yes, she does.
Is this your book?
Yes, it's my book.
Yes, it's your book.
Is your brother playing hockey?
Yes, he is.
Yes, she is.
Does your nephew go to school?
Yes, he does.
Yes, she does.
What is your father doing?
He's working.
Yes, he is.
Is your aunt studying English?
No, he isn't.
No, she isn't.
What are you doing?
I'm studying English.
You're studying English.
Is your sister using your computer?
Yes, she does.
Yes, she is.
Now, I am playing my guitar
My girlfriend is working in the disco today
I am not studying at the moment
Are you listening to me?
Hi there! I'm The Present Continuous Guy. I'm here to tell you what I'm doing at the moment because my life is changing a lot these days. Now I'm not studying, but I'm working in a Body Piercing Tattoo shop. I like tattoos. At the moment I'm wearing nine tattoos and ten piercings.
At present I'm playing the guitar in a heavy metal group called "Metal Bananas".
This evening I' m playing with some friends in Marbella in a birthday party. I' m going out with a girl, but she's working in the disco today. She isn't coming with me to the party. Are you coming with me guys?
Si quieres aprender cómo se forma y cuándo se usa el Present Continuous haz click en los siguientes apartados:
Practica lo aprendido con los siguientes ejercicios:
"Let's practise"
Form
Use
Contrast
The men are not playing. they are working.
Is the dog drinking beer?
No, It is smoking a cigar.
Con la mayoría de los verbos sólo se agrega -ING, pero con otros necesita hacer algunos cambios, aqui estan las reglas:hit - hitting get - getting | ||
lose - losing live - living | ||
go - going walk - walking |
Noten como en el uso informal –oral- sustituye la “g” del final del gerundio por una apostrofe.
En las canciones las palabras sufren algunas leves modificaciones, pero aún asi puedes reconocer el Presente Continuo en esta letra. de Barry Manilow
Para ver más sobre los diversos tiempos verbales en inglés ve a estos enlaces:
- Learn English Tenses - English Grammar - Present Tenses Review of Auxiliary...
- Present tense - definition and examples of present tense
- English Learning Terms - Tenses - Present Perfect Continuous
- Learn English Tenses - English Grammarfor ESL TESOL Students and Teacher
- http://www.edufind.com/english/grammar/Tenses3.cfm
- http://www.ejerciciodeingles.com/tag/present-continuous/